📢 この記事は gemini-2.5-flash によって翻訳されました
Interpreter Pattern クラスの振る舞いパターン
どんなこと?
ある言語があったとき、その文法を表す方法を定義して、その表現を使って言語の文を解釈するインタプリタも定義するんだ。
構造
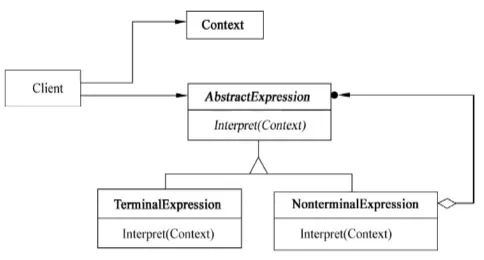
こんな感じだよ:
- AbstractExpression はプログラムの解釈操作を宣言するインターフェースで、これは抽象構文木のすべてのノードで共有されるものなんだ。
- TerminalExpression は文法の終端記号に関連する解釈操作を実装するよ。文中の各終端記号には、このクラスのインスタンスが一つ必要になるんだ。
- NonterminalExpression は、文法の各ルールごとに NonterminalExpression クラスが必要になるよ。各記号に対して AbstractExpression 型のインスタンス変数を一つずつ持ってて、文法の非終端記号の解釈 (Interpret) 操作を実装するんだ。
- Context は、インタプリタ以外のグローバルな情報を含むものだよ。
- Client は、その文法で定義された言語の特定の文を表す抽象構文木を構築する (または与えられる) んだ。この抽象構文木は NonterminalExpression と TerminalExpression のインスタンスを組み合わせて作られるよ。そして、解釈操作を呼び出すんだ。
いつ使うといいの?
インタプリタパターンは、解釈実行が必要な言語があって、その言語の文を抽象構文木として表せる場合に役立つよ。特に、次の状況で一番うまくいくんだ:
例を見てみよう
文字列をチェックする例だよ:「某区の某人員 (someone of ? region)」
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| import java.util.*;
public class InterpreterPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Context context = new Context();
context.check("developer of A region");
}
}
class Context{
private String[] regions = {"A region", "B region", "C region"};
private String[] persons = {"developer", "tester"};
private NonterminalExpression nte;
public Context(){
TerminalExpression region = new TerminalExpression(regions);
TerminalExpression person = new TerminalExpression(persons);
nte = new NonterminalExpression(region, person);
}
public void check(String info){
boolean bool = nte.Interpret(info);
if(bool){
System.out.println("right");
}else {
System.out.println("wrong");
}
}
}
interface Expression{
public boolean Interpret(String info);
}
class NonterminalExpression implements Expression{
TerminalExpression region;
TerminalExpression person;
public NonterminalExpression(TerminalExpression region, TerminalExpression person){
this.person = person;
this.region = region;
}
@Override
public boolean Interpret(String info){
String[] str = info.split(" of ");
// "developer of A region" --> str = {"developer", "A region"}
return region.Interpret(str[1]) && person.Interpret(str[0]);
}
}
class TerminalExpression implements Expression{
private Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
public TerminalExpression(String[] data){
for(String str : data){
set.add(str);
}
}
@Override
public boolean Interpret(String info){
return set.contains(info);
}
}
|
