📢 This article was translated by gemini-3-flash-preview
Iterator Pattern - Object Behavioral Pattern
Intent
Provide a way to access the elements of an aggregate object sequentially without exposing its underlying representation.
Structure
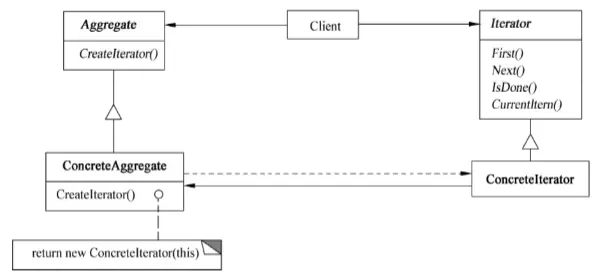
Participants:
- Iterator: Defines an interface for accessing and traversing elements.
- ConcreteIterator: Implements the Iterator interface and keeps track of the current position in the traversal.
- Aggregate: Defines an interface for creating an Iterator object.
- ConcreteAggregate: Implements the Iterator creation interface to return an instance of the appropriate ConcreteIterator.
Applicability
Use the Iterator pattern when:
- You need to access an aggregate object’s contents without exposing its internal structure.
- You need to support multiple types of traversals for aggregate objects.
- You want to provide a uniform interface for traversing different aggregate structures.
Using Java’s Built-in Iterator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class IteratorPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Book> bookList = new ArrayList<>();
String[] books = {"Linear Algebra", "Algorithm"};
double[] prices = {25.8, 29.8};
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++){
bookList.add(new Book(books[i], prices[i]));
}
// Access elements 1
for(int i = 0; i < bookList.size(); i++){
Book book = bookList.get(i);
System.out.println("name: " + book.getName() + " price: " + book.getPrice());
}
// Access elements 2
System.out.println("=====222=====");
for(Book book : bookList){
System.out.println("name: " + book.getName() + " price: " + book.getPrice());
}
// Access elements 3 (Iterator)
System.out.println("=====333=====");
Iterator iterator = bookList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Book book = (Book) iterator.next();
System.out.println("name: " + book.getName() + " price: " + book.getPrice());
}
}
}
class Book{
private String name;
private double price;
public Book(String name, double price){
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
|
Example Implementation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
| import javax.sound.midi.Soundbank;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class IteratorPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookAggregate bookAggregate = new BookAggregate();
String[] books = {"Linear Algebra", "Algorithm"};
double[] prices = {25.8, 29.8};
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++){
bookAggregate.Add(new Book(books[i], prices[i]));
}
Iterator iterator = bookAggregate.CreateIterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Book book = (Book)iterator.next();
System.out.println("name: " + book.getName() + " price: " + book.getPrice());
}
}
}
interface Iterator{
public boolean hasNext();
public Object next();
}
class BookIterator implements Iterator{
private int index;
private BookAggregate bookAggregate;
public BookIterator(BookAggregate bookAggregate){
this.index = 0;
this.bookAggregate = bookAggregate;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext(){
if (index < bookAggregate.getSize()) return true;
return false;
}
@Override
public Object next(){
Object obj = bookAggregate.get(index);
index++;
return obj;
}
}
interface Aggregate{
public Iterator CreateIterator();
}
class BookAggregate implements Aggregate{
private List<Book> list = new ArrayList<>();
public void Add(Book book){
list.add(book);
}
public Book get(int index){
return list.get(index);
}
public int getSize(){
return list.size();
}
@Override
public Iterator CreateIterator(){
return new BookIterator(this);
}
}
class Book{
private String name;
private double price;
public Book(String name, double price){
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
|
