📢 This article was translated by gemini-2.5-flash
Command Pattern: A Behavioral Design Pattern
Intent
Encapsulate a request as an object, allowing clients to be parameterized with different requests. It supports request queuing, logging, and undoable operations.
Structure
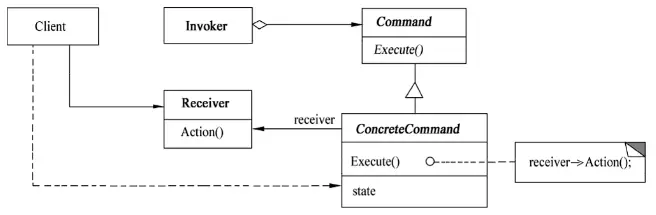
Here’s the breakdown:
- Command: Declares an interface for executing an operation.
- ConcreteCommand: Binds a Receiver object to an action; invokes the Receiver’s corresponding operation to implement Execute.
- Client: Creates a concrete command object and sets its receiver.
- Invoker: Asks the command to carry out the request.
- Receiver: Knows how to perform the operations associated with a request. Any class can act as a receiver.
Applicability
The Command pattern is useful when you need to:
- Abstract an action to be performed, parameterizing an object.
- Specify, queue, and execute requests at different times.
- Support undo operations.
- Support logging changes.
- Construct a system using high-level operations built on primitive operations.
Example
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
| public class CommandPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Receiver object: TV
Tv tv = new Tv();
// Command objects
Command oncommand = new OnCommand(tv);
Command offcommand = new OffCommand(tv);
// Invoker
Invoker invoker = new Invoker();
// Turn on
invoker.setCommand(oncommand);
invoker.Execute();
// Turn off
invoker.setCommand(offcommand);
invoker.Execute();
}
}
class Invoker{ // Invoker
private Command command; // Command
public void setCommand(Command command){ // Set the invoker's command
this.command = command;
}
public void Execute(){ // Execute the command
command.Execute();
}
}
interface Command{ // Command interface
public void Execute(); // Execute command
}
class OnCommand implements Command{ // Turn on command
private Tv tv;
public OnCommand(Tv tv){
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void Execute(){
tv.OnAction();
}
}
class OffCommand implements Command{ // Turn off command
private Tv tv;
public OffCommand(Tv tv){
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void Execute(){
tv.OffAction();
}
}
class Tv{ // Receiver: TV
public void OnAction(){
System.out.println("Tv On");
}
public void OffAction(){
System.out.println("Tv Off");
}
}
|
