📢 This article was translated by gemini-2.5-flash
Chain of Responsibility Pattern (Object Behavioral Pattern)
Intent
Decouple the sender of a request from its receiver by giving multiple objects a chance to handle the request. Link these objects into a chain and pass the request along the chain until an object handles it.
Structure
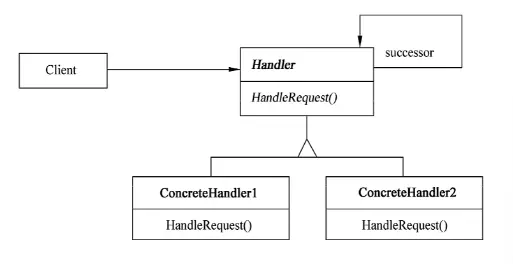
Here’s the breakdown:
- Handler: Defines an interface for handling requests; (Optional) implements the successor link.
- ConcreteHandler: Handles requests it’s responsible for; can access its successor. If it can handle the request, it does; otherwise, it forwards it to the successor.
- Client: Submits requests to a ConcreteHandler object in the chain.
Applicability
Apply the Chain of Responsibility pattern when:
- Multiple objects can handle a request, and the specific handler is determined at runtime.
- You want to issue a request to one of several objects without explicitly specifying the receiver.
- The set of objects that can handle a request should be specifiable dynamically.
Example
A student asks for leave: first to the counsellor. If the counsellor can’t approve, it goes to the dean. If the dean can’t approve, it goes to the principal.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
| public class ChainOfResponsibilityPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Instantiate objects
Handler counsellor = new Counsellor();
Handler president = new President(); // Represents the Dean
Handler schoolmaster = new Schoolmaster(); // Represents the Principal
// Set the next handler in the chain
counsellor.next = president;
president.next = schoolmaster;
schoolmaster.next = null;
// Request 7 days of leave from the counsellor
counsellor.HandlerRequest(7);
}
}
abstract class Handler{
protected Handler next;
public void setNext(Handler next){
this.next = next;
}
// Student leave request
public abstract void HandlerRequest(int request);
}
class Counsellor extends Handler{
// Counsellor: Approves <= 7 days
@Override
public void HandlerRequest(int request){
if (request <= 7) {
System.out.println("Counsellor Agree!");
}
else {
if(next != null){
next.HandlerRequest(request);
}
else {
System.out.println("Counsellor Refuse!");
}
}
}
}
class President extends Handler{
// Dean: Approves <= 15 days
@Override
public void HandlerRequest(int request){
if (request <= 15) {
System.out.println("President Agree!");
}
else {
if(next != null){
next.HandlerRequest(request);
}
else {
System.out.println("President Refuse!");
}
}
}
}
class Schoolmaster extends Handler{
// Principal: Approves <= 30 days
@Override
public void HandlerRequest(int request){
if (request <= 30) {
System.out.println("Schoolmaster Agree!");
}
else {
if(next != null){
next.HandlerRequest(request);
}
else {
System.out.println("Schoolmaster Refuse!");
}
}
}
}
|
