📢 This article was translated by gemini-3-flash-preview
Flyweight Pattern - Structural Pattern
Intent
Use sharing to support large numbers of fine-grained objects efficiently.
Structure
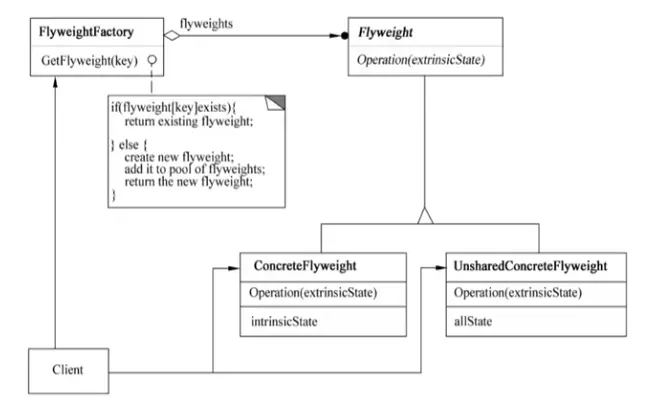
Participants:
- Flyweight: Declares an interface through which flyweights can receive and act on extrinsic state.
- ConcreteFlyweight: Implements the Flyweight interface and adds storage for intrinsic state, if any. ConcreteFlyweight objects must be sharable. Any state it stores must be intrinsic (independent of the object’s context).
- UnsharedConcreteFlyweight: Not all Flyweight subclasses need to be shared. The Flyweight interface enables sharing, but doesn’t force it. UnsharedConcreteFlyweight objects often have ConcreteFlyweight objects as children.
- FlyweightFactory: Creates and manages flyweight objects. Ensures that flyweights are shared properly. When a client requests a flyweight, the factory provides an existing instance or creates one if it doesn’t exist.
- Client: Maintains a reference to flyweights and computes or stores their extrinsic state.
Applicability
Use the Flyweight pattern when:
- An application uses a large number of objects.
- Storage costs are high because of the quantity of objects.
- Most object state can be made extrinsic.
- Many groups of objects may be replaced by relatively few shared objects once extrinsic state is removed.
- The application doesn’t depend on object identity. Since flyweight objects may be shared, identity tests will return true for conceptually distinct objects.
Example 1
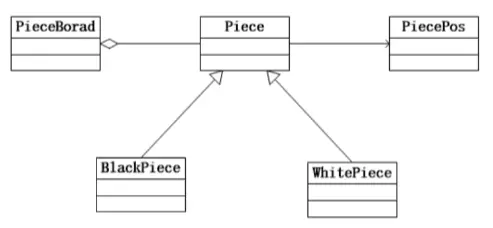
Developing an online Go (Weiqi) program that allows multiple players. To save memory on a single server, the Flyweight pattern is used. Here is the class diagram:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
| import java.util.ArrayList;
enum PieceColor {BLACK, WHITE} // Piece color
class PiecePods{ // Piece position
private int x;
private int y;
public PiecePods(int a, int b){
x = a;
y = b;
}
public int getX(){
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
}
abstract class Piece{ // Piece definition
protected PieceColor m_color; // Color
protected PiecePods m_pos; // Position
public Piece(PieceColor color, PiecePods pos){
this.m_color = color;
this.m_pos = pos;
}
public abstract void draw();
}
class BlackPiece extends Piece{
public BlackPiece(PieceColor color, PiecePods pos){
super(color, pos);
}
@Override
public void draw(){
System.out.println("Draw a black piece");
}
}
class WhitePiece extends Piece{
public WhitePiece(PieceColor color, PiecePods pos){
super(color, pos);
}
@Override
public void draw(){
System.out.println("Draw a white piece");
}
}
class PieceBoard{ // Existing pieces on the board
private static final ArrayList<Piece> m_arrayPiece = new ArrayList<>();
private String m_blackName; // Black player name
private String m_whiteName; // White player name
public PieceBoard(String black, String white){
m_blackName = black;
m_whiteName = white;
}
// A move: placing a piece on the board
public void setPiece(PieceColor color, PiecePods pos){
Piece piece = null;
if(color == PieceColor.BLACK){ // Place black piece
piece = new BlackPiece(color, pos);
System.out.println(m_blackName + pos.getX() + pos.getY());
piece.draw();
}else{ // Place white piece
piece = new WhitePiece(color, pos);
System.out.println(m_whiteName + pos.getX() + pos.getY());
piece.draw();
}
m_arrayPiece.add(piece);
}
}
|
Example 2
Gomoku (Five-in-a-Row)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| public class FlyWeightPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PieceFactory factory = new PieceFactory();
Piece wp1 = factory.getPiece(0);
wp1.draw(2023, 0527);
}
}
class PieceFactory{
private Piece[] pieces = {new WhitePiece(), new BlackPiece()};
public Piece getPiece(int key){
if(key == 0) return pieces[0];
else return pieces[1];
}
}
abstract class Piece{
protected String color;
public abstract void draw(int x, int y);
}
class WhitePiece extends Piece{
public WhitePiece(){
this.color = "white";
}
@Override
public void draw(int x, int y){
System.out.println("draw a " + this.color + " piece x: " + x + " y: " + y);
}
}
class BlackPiece extends Piece{
public BlackPiece(){
this.color = "Black";
}
@Override
public void draw(int x, int y){
System.out.println("draw a " + this.color + " piece x: " + x + " y: " + y);
}
}
|
Example 3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
public class FlyWeightPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeFactory sf = new ShapeFactory();
Random r = new Random();
String[] colors = {"red", "blue", "green", "white", "black"};
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int x = r.nextInt(colors.length);
Shape s = sf.getShape(colors[x]);
s.draw(r.nextInt(2023), r.nextInt(527));
}
}
}
class ShapeFactory{
private Map<String, Shape> map = new HashMap<>();
public Shape getShape(String key){
if (!map.containsKey(key)) {
map.put(key, new Circle(key));
System.out.println("create new circle, color: " + key);
}
return map.get(key);
}
}
abstract class Shape{
protected String color;
public abstract void draw(int x, int y);
}
class Circle extends Shape{
public Circle(String color){
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public void draw(int x, int y) {
System.out.println("draw a " + this.color + " circle x: " + x + " y: " + y);
}
}
|

